
Brain Information Processing Based Intelligent System
Intelligent Machine Learning Laboratory (IML Lab)
Research Description
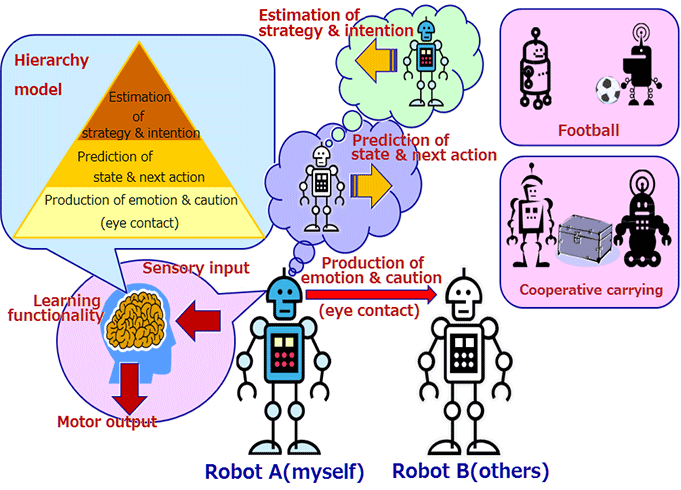
Figure: Outline of Brain Information Based Intelligent System
When humans perform cooperative actions, including playing group sports, such as soccer, or working together to carry loads, they act successfully by cooperating with others in order to achieve their common goals using various means of communication, including language, body language, or making eye contact. Industrial robots working in factories or entertainment robots on the market operate passively according to the action plans given by designers (humans); therefore, it still poses a very challenging problem to make robots (computers) perform such cooperative actions.
The Strategic Technology Roadmap (published in 2010) by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry points out that service robots (introduced to service industries) are behind in practical application. One of the main reasons is said to be that we are still behind in developing an intelligent robot technology that ensures robot operation under variable or dynamic environments including outdoor and living spaces.
This lab seeks to approach the intelligent robot technology from both theoretical and practical aspects across various disciplines, including brain science, life science, cognitive science, complex systems science, and control engineering. Firstly, therefore, it pays attention to the fact that humans gain their behaviors primarily by receiving sensory input from external environments under changing situations through the five sensory organs and actively learning at the same time through interactions with others to present appropriate motor outputs to the outside environments corresponding to such situations. Secondly, it conducts research in order to realize advanced intelligent actions, including cooperative actions by using an intelligent system imitating such brain information processing functions.
The lab proposes a hypothesis that humans process brain information in three-layer hierarchical models as shown in the figure, consisting of an emotion/attention generating model, state/action estimating model, and policy/intention estimating model. It also pays attention to non-communication including prediction of state/action and estimation of policy/intention of others, as well as communication by eye contact, to develop a brain information processing based intelligent system (refer to the figure) as integrating these models. It proposes as the ultimate goal to make robots instinctively perform cooperative actions in the future without communication with others.
Research subjects
- Modeling a multi-agent system mechanism to predict actions and estimate intentions of others
- Constructing a next-generation human-robot interaction system using a "dividual" model
- Constructing a brain information processing based intelligent system using an artificial intelligence-type cloud network
Keywords
Multi-agent system, intention estimation, cooperative action, human-robot interaction, machine learning, artificial intelligence, cloud network, brain information processing, reinforcement learning, neural network, intelligent system

